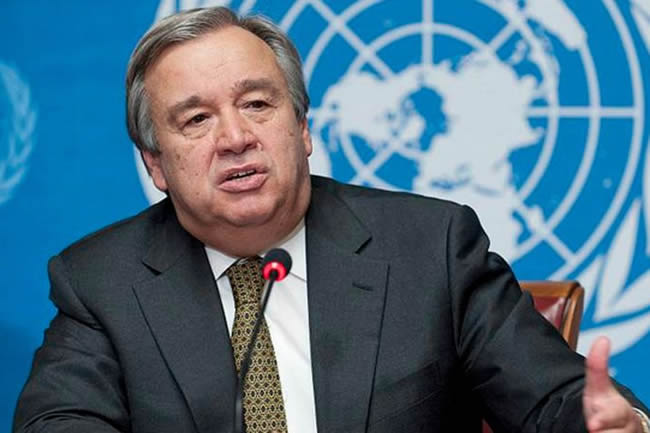
The UN Secretary-General recently warned that a widespread hunger crisis will affect different parts of the world due to Russia’s war in Ukraine, and Putin is now using a blockade of grain exports as blackmail against the world. The writer offers some perspectives on averting this disaster.
A global food crisis is looming, so policymakers everywhere need to think hard about how to make food cheaper and more plentiful. That requires making a commitment to producing more fertiliser and better seeds, maximising the potential offered by genetic modification and abandoning the rich world’s obsession with organics.
Russia’s brutal war in Ukraine is making less food available because the two nations have been responsible for more than a quarter of global wheat exports and big quantities of barley, corn and vegetable oil. On top of punishing climate policies and the world emerging from the pandemic, prices of fertiliser, energy and transport are soaring, and food prices have climbed 61 per cent over the past two years.
Harsh truths
The war has exposed some harsh truths. One is that Europe – which portrays itself as a green energy trailblazer – is highly reliant on Russian gas, especially when the sun is not shining or the wind is not blowing.
The war has reaffirmed the basic reality that fossil fuels remain crucial for the vast majority of global needs. And the emerging food crisis now reveals another harsh truth: organic farming cannot feed the world and could even worsen future crises.
Long simply a fashionable trend for the world’s one per cent, environmental activists have increasingly peddled the beguiling idea that organic farming can solve hunger. The European Union is actively pushing for a tripling of organic farming on the continent by 2030, while a majority of Germans actually think organic farming can help feed the world.
However, research conclusively shows that organic farming produces much less food than conventional farming per hectare. Moreover, organic farming requires farmers to rotate soil out of production for pasture, fallow or cover crops, reducing its effectiveness.
In total, organic approaches produce between a quarter and half less food than conventional, scientific-driven agriculture.
This not only makes organic food more expensive, but it means that organic farmers will need much more land to feed the same number of people as today – possibly almost twice the area. Given that agriculture currently uses 40 per cent of Earth’s ice-free land, switching to organics will mean destroying large swathes of nature for less effective production.
Sobering lesson
The catastrophe unfolding in Sri Lanka provides a sobering lesson. The government, last year, enforced a full transition to organic farming, appointing organics gurus as agricultural advisors, including some who claimed dubious links between agricultural chemicals and health problems. Despite extravagant claims that organic methods could produce comparable yields to conventional farming, within months, the policy produced nothing but misery, with some food prices quintupling.
Sri Lanka had been self-sufficient in rice production for decades, but tragically has now been forced to import $450 million worth of rice. Tea, the nation’s primary export crop and source of foreign exchange, was devastated, with economic losses estimated at $425 million.
Before the country spiraled downward toward brutal violence and political resignations, the government was forced to offer $200 million in compensation to farmers and come up with $149 million in subsidies.
Failed
Sri Lanka’s organic experiment failed fundamentally because of one simple fact: it does not have enough land to replace synthetic nitrogen fertiliser with animal manure. To shift to organics and keep production, it will need five to seven times more manure than its total manure today.
Synthetic nitrogen fertilisers, mostly made with natural gas, are a modern miracle, crucial for feeding the world. Largely, thanks to this fertiliser, agricultural outputs were tripled in the past half-century, as the human population doubled.
Artificial fertiliser and modern farming inputs are the reason why the number of people working on farms has been slashed in every rich country, freeing people for other productive occupations.
In fact, one dirty secret of organic farming is that, in rich countries, the vast majority of existing organic crops depend on imported nitrogen laundered from animal manure, which ultimately comes from fossil fuel fertilisers used on conventional farms.
Without those inputs, if a country – or the world – were to go entirely organic, nitrogen scarcity quickly becomes disastrous, just like we saw in Sri Lanka. That is why research shows that going organic globally can only feed about half the current world population. Organic farming will lead to more expensive, scarcer food for fewer people, while gobbling up more nature.
To sustainably feed the world and withstand future global shocks, we need to produce food better and cheaper.
History shows that the best way to achieve that is by improving seeds, including using genetic modification, along with expanding fertiliser, pesticides and irrigation. This will allow us to produce more food, curb prices, alleviate hunger and save nature.
The writer is President of the Copenhagen Consensus and Visiting Fellow at Stanford University’s Hoover Institution. His latest book is “False Alarm.”
By Bjorn Lomborg