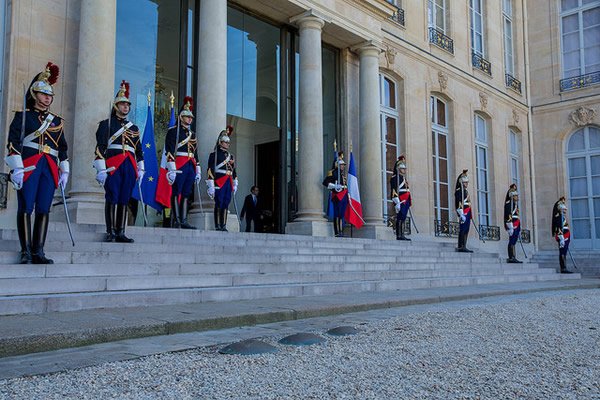
President Joe Biden will seek to grow his “close relationship” with the United Kingdom, the White House says, when he pays his first visit to newly crowned King Charles III and meets with Britain’s political leader to strengthen the bond between the two nations ahead of a critical NATO summit that could determine the course of the conflict in Ukraine.
London is the first stop on Biden’s three-nation tour, which begins Monday. He will then go to Vilnius, Lithuania’s capital, for a summit of NATO leaders, and then to Helsinki, the capital city of NATO’s newest member, Finland.
“The president is very much looking forward to this,” John Kirby, spokesperson for the National Security Council, told VOA. “As you know, the United Kingdom is our strongest ally, in so many ways, on so many levels.”
Kirby said Biden will discuss issues such as the war in Ukraine with Prime Minister Rishi Sunak and will discuss environmental challenges with the monarch, who was an early advocate for climate action.
“Not to downplay the U.K. trip, but this is not a full-fledged visit to the country but rather a stop on the way to Lithuania,” Dalibor Rohac, a resident scholar at the American Enterprise Institute, told VOA, via email.
And, he said, London noticed when Biden heaped praise on his ancestral home of Ireland, which he has described as “part of his soul.” The southern two-thirds of the Irish island is not part of the United Kingdom and has historically opposed the monarchy.
“For a host of reasons, British Conservative commentariat and political class feel constantly slighted by Biden – from his expressions of Irishness, through his absence at the king’s coronation, to Ben Wallace’s unsuccessful bid to lead NATO,” Rohac said. “That sense of neglect and of being snubbed is not going away, even if Rishi Sunak’s personal relationship with Biden appears good and even if the U.K. and the U.S. work extremely closely on a range of topics from Ukraine to security in the Indo-Pacific.”
Still, there is some symbolism to the American leader meeting amicably with the British king. Charles III is a direct descendant of King George III, the distant sovereign against whom a group of American colonists leveled a litany of complaints in the Declaration of Independence.
“So it’s to kind of recognize the pomp and circumstance of the unique head of state in the U.K. and of course, the unique history between these two great nations,” said Sean Monaghan, a visiting fellow with the Center for Strategic and International Studies.
“But also on a more substantive policy front, President Biden has met with Prime Minister Rishi Sunak a number of times in recent months, and they will be looking to move forward that agenda that they agreed recently, during Sunak’s last visit here, the so called Atlantic Declaration, which promises closer cooperation on a range of issues from trade, to defense, and elsewhere.”
Commonwealth changing
King Charles III remains head of state – mostly in a ceremonial sense – for more than 2.6 billion people, spread across the globe as citizens of the 56 Commonwealth nations. The voluntary political association consists mostly of former territories of the British Empire. Their collective goals include supporting democracy, government and the rule of law and promoting liberal values like gender equality. The United States is not a member, but 13 nations in the Americas are.
In recent years, members have questioned Britain’s right to rule them and interrogated their painful colonial past. Constitutional scholar Richard Albert is a member of Jamaica’s constitutional reform committee, which will help the nation set up a post-Commonwealth framework.
Albert, a law professor at the University of Texas at Austin, said he recently returned from a trip to New Zealand – another Commonwealth member state – where “they corrected me when I called it the Commonwealth,” he said.
“They called it the Commontheft, the idea being that the Commonwealth has gained and accumulated all of its power and money on theft, of peoples, of lands, of possessions, of culture,” he told VOA. “And so I thought that was a very powerful statement on the part of the people there in New Zealand.”
The king, in his first Commonwealth Day message earlier this year, described the alliance as “an association not just of shared values, but of common purpose and joint action.”
“Its near-boundless potential as a force for good in the world demands our highest ambition; its sheer scale challenges us to unite and be bold,” he said.
Albert, who is Canadian – and who supports the idea of Ottawa withdrawing from the group – said “it’s possible to imagine the Commonwealth now and into the future, being a force for good for democracy, for constitutionalism, for the rule of law.”
But first, he says, something big has to happen.
“I wish the president would ask the king whether he plans to make amends for the wrongdoings of the monarchy over the past centuries,” he said. “But of course, if the president were to ask King Charles that, he’d have to ask himself the very same question, wouldn’t he?”
Source: voanews.com